

Convert the Kelvin temperature to degrees Celsius.Ģ. On thermometers used in school laboratories and weather agencies, the temperature is usually displayed in Celsius.The process of using this equation to convert Kelvin to Celsius is as follows:ġ. Because of its range of convenience, the Celsius scale is preferred by common people all across the world over the Kelvin scale. To name a few instances, boiling water, freezing water, and the temperature of our refrigerator at home or in cold storage. The scale begins and operates in the temperature range with which we are most accustomed. We conclude that The Celsius scale is used in everyday life by people all around the world.
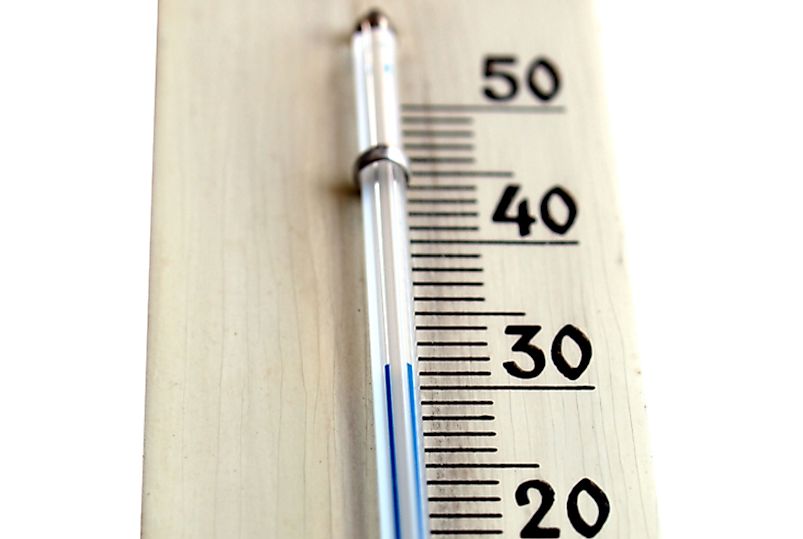

Similarly, this indicates that the lowest attainable Celsius temperature is – 273.15 C. It is the point in a system where no more heat can be eliminated because there is no molecular movement, and hence no lower temperature is feasible. Absolute zero is sometimes known as zero K. While negative numbers for Celsius temperatures are totally common, the Kelvin scale only goes down to zero. The Kelvin scale is the international standard for measuring scientific temperature and is used in many domains, including astronomy and physics. The Kelvin scale is based on energy measurement and begins at absolute zero (the coldest temperature attainable) (the movement of molecules). While most temperatures in everyday life are stated in Celsius or Fahrenheit, many phenomena are better described using an absolute temperature scale. Water has a boiling point of 100 degrees Celsius. Let’s say you want to convert the boiling point of water to Kelvin. You can use either the aforementioned formula or K = C + 273.15. Similarly, converting a Celsius temperature to the Kelvin scale is simple. Temperature conversion from Celsius to Kelvinĭespite the fact that we know the correct conversion number is 273.15, we frequently remove the decimal component and use 273. We may convert temperature from one scale to another using these simple equations. However, a temperature change of one degree Fahrenheit does not equal a temperature change of one degree Celsius. In addition, 0° C is a warmer temperature than 0°. A 1° Kelvin shift, on the other hand, is equivalent to a 1° Celsius change. As can be seen, 0° C is a far higher temperature than 0° K. Water has a freezing point of 32 degrees Fahrenheit (0 degrees Celsius) or 273 degrees Kelvin. Changing from Celsius to Kelvin Temperature Conversions The Kelvin scale is another centigrade scale. Consider the Celsius scale as an example of a centigrade scale. A centigrade scale has 100 steps, identical to the degree units used to express the difference in temperature between freezing and boiling water.
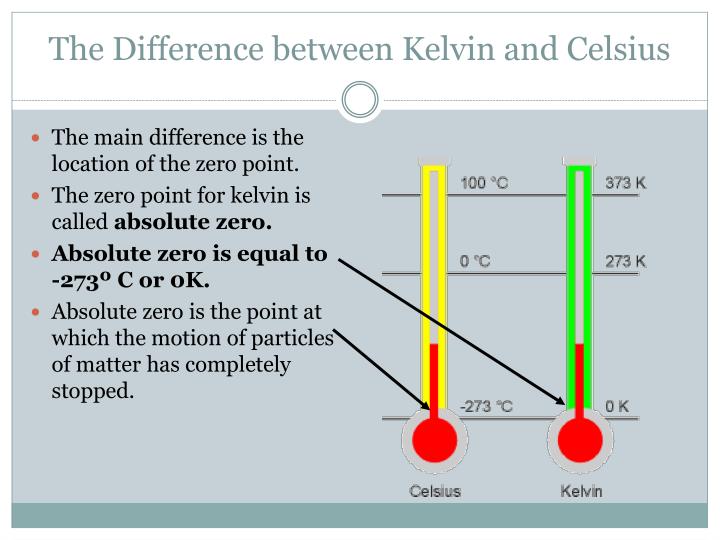
However, the terms Celsius and centigrade do not have the same meaning. Until 1948, the scale was known as the centigrade scale before being renamed Celsius. A Swedish astronomer devised this temperature scale. The Celsius scale is named after Anders Celsius. Furthermore, because the Kelvin scale is an absolute scale, no degree is necessary. Temperature ranges of one degree Celsius and one degree Kelvin are the same. The triple point of water is 273.16 K, which is 0.01° C or 32.02°. This simplifies the conversion of temperature scales from Celsius to Kelvin, and absolute zero is defined as 0 K and – 273.15°. To be more specific, the Celsius scale is determined by absolute zero and the triple point of pure water. The Kelvin temperature scale is the official temperature scale, and the Celsius temperature scale is a common System International (SI) temperature scale. Because the temperature difference between the two fixed places is 100 degrees Celsius, this thermometer scale is also known as the centigrade scale. The boiling point of water is 100 degrees Celsius, or 100°. Water’s freezing point on this scale is 0 degrees Celsius, or 0°. It lies midway between the freezing and boiling points of water. The centigrade scale is divided into 100 equal parts known as degrees Celsius. In physics, the Celsius scale is most widely employed in comparison to other temperature scales. The same temperature has different readings on the three temperature scales – Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin. Temperature is typically stated as a numerical value on a standard scale. Temperature is a critical physical quantity that shows how hot or cold something is.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
